In an era where organic traffic drives the lion’s share of online engagement, mastering search engine optimization (SEO) is non-negotiable. This guide unpacks what SEO is, traces its history of evolution, and delves into the seminal PageRank algorithm. You’ll discover how SEO works today and why SEO Matters, explore core components—on-page, technical, and off-page—and learn advanced tactics like voice search optimization and AI-driven SEO. Let’s dive in.
1. What Is SEO?

SEO—short for search engine optimization—is the practice of enhancing a website’s content, structure, and authority to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). Unlike paid ads, SEO focuses on organic visibility, attracting users actively seeking information, products, or services. Effective SEO boosts brand credibility, drives sustained ROI, and positions your site for long-term growth.
2. Early Days: History of Search Engine Optimization
- 1990s: Keyword Wild West
Early engines (AltaVista, Excite) ranked pages by keyword density, leading to rampant keyword stuffing. - 1998: Yahoo! Directory & Google’s Launch
Yahoo! relied on human-curated listings; Google introduced PageRank, valuing backlink profile over mere keywords. - 2000s: Metadata & Link Farming
Webmasters manipulated meta keywords and built link farms until Google’s Panda and Penguin updates penalized low-quality tactics.
3. Google’s Rise & the PageRank Breakthrough
Developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the PageRank algorithm revolutionized relevance:
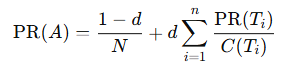
- d: Damping factor (~0.85)
- Tᵢ: Pages linking to A
- C(Tᵢ): Outbound links on Tᵢ
PageRank emphasized link authority, laying the groundwork for today’s complex ranking signals.
4. Algorithm Evolution: From Panda to BERT
Google’s algorithm has matured to reward quality and relevance:
| Update | Year | Focus |
| Panda | 2011 | Penalize thin, low-value content |
| Penguin | 2012 | Crack down on spammy link schemes |
| Hummingbird | 2013 | Semantic search, user intent |
| Mobile-First Indexing | 2018 | Prioritize mobile responsiveness |
| BERT | 2019 | Natural language processing & context |
| Helpful Content | 2022 | User-first content emphasis |
Each update underscores the shift toward user intent, semantic SEO, and content excellence.
5. How SEO Works Today: Crawling, Indexing & Ranking
- Crawling
Bots traverse links and XML sitemaps to discover content. Ensure your robots.txt doesn’t block key pages. - Indexing
Search engines parse HTML, JavaScript, and structured data (Schema markup) to understand page context. - Ranking
Hundreds of signals—page speed, Core Web Vitals, backlinks, and user engagement metrics (bounce rate, dwell time)—determine SERP order.
6. Core Components of Modern SEO
6.1 On-Page SEO Essentials
- Keyword Strategy: Integrate short-tail, long-tail, and LSI keywords (e.g., “what is SEO and how it works”, “search engine optimization history”) naturally in titles, headings, and body copy.
- Meta Elements: Craft compelling <title> tags (≤60 chars) and meta descriptions (≤155 chars) to improve CTR.
- Content Structure: Use H1–H3 hierarchy for readability; employ bullet lists and bold key terms for skimmability.
- Media Optimization: Add descriptive alt text and compress images; optimize videos with Schema VideoObject markup.
6.2 Technical SEO Foundations
- Site Speed & Core Web Vitals: Optimize caching, minify CSS/JS, implement lazy loading to improve Largest Contentful Paint and First Input Delay.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Use responsive design and test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Structured Data: Implement BreadcrumbList, Website, FAQPage, and other Schema to enable rich results and AI Overviews.
- Security & HTTPS: Ensure SSL certificates are valid; migrate all HTTP pages to HTTPS.
6.3 Off-Page SEO & Link Authority
- Backlink Building: Pursue high-quality links via digital PR, guest posting, and HARO; monitor your backlink profile in Ahrefs or Moz.
- Brand Mentions & Citations: Secure consistent business listings for local SEO; encourage reviews on Google Business Profile.
- Social Signals: Share content on platforms to amplify reach and attract organic links.
7. Advanced Trends in SEO
- AI-Driven Search & Generative Overviews
Optimize for AI Overviews by structuring content in clear Q&A or numbered formats—Google’s models favor concise, authoritative answers. - Voice Search Optimization
Target conversational queries (“how do I set up robots.txt?”) and implement FAQPage schema to capture voice assistant traffic. - Video & Image SEO
Create standalone pages for videos; use Schema VideoObject and image captions to appear in image packs and video carousels.
8. Crafting an Effective Keyword Strategy
- Seed & Expand: Start with core topics (“SEO basics”), then use tools—Google Keyword Planner, AnswerThePublic, SEMrush—to uncover long-tail keywords.
- Cluster Approach: Group related keywords into pillar and cluster topics; use internal linking to reinforce topic authority.
- Intent Mapping: Categorize queries as informational, navigational, or transactional, and tailor content accordingly.
9. Measuring SEO Success: Key Metrics
| Metric | Description |
| Organic Traffic | Visits from unpaid search—primary indicator of reach |
| CTR | Clicks ÷ impressions—signals effectiveness of snippets |
| Conversion Rate | Goal completions per visit—ties SEO to ROI |
| Bounce Rate | % single-page sessions—measures relevance |
| Dwell Time | Time on page—reflects engagement |
| Keyword Rankings | Positions for target keywords—monitored over time |
| Backlink Profile | Quantity & quality of inbound links—authority gauge |
10. White Hat SEO vs. Black Hat SEO
- White Hat SEO: Ethical, user-first techniques—high-quality content, natural link building, compliance with guidelines.
- Black Hat SEO: Risky shortcuts—cloaking, spam links, keyword stuffing—that can lead to penalties or deindexing.
- Best Practice: Embrace E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) by citing sources, showcasing credentials, and updating content regularly.
Conclusion
This Definitive “What Is SEO?” Guide has walked you through the history, evolution, and foundational PageRank algorithm, explained how SEO operates today, and laid out actionable strategies across on-page, technical, and off-page realms. By integrating short-tail, long-tail, and LSI keywords, optimizing for Core Web Vitals, and embracing advanced trends like AI Overviews and voice search, you’re equipped to drive sustainable organic traffic, enhance brand authority, and future-proof your digital presence. Next up, dive into Keyword Research & Content Strategy—where you’ll learn to uncover high-value search queries and map out a content calendar that amplifies your SEO impact.





